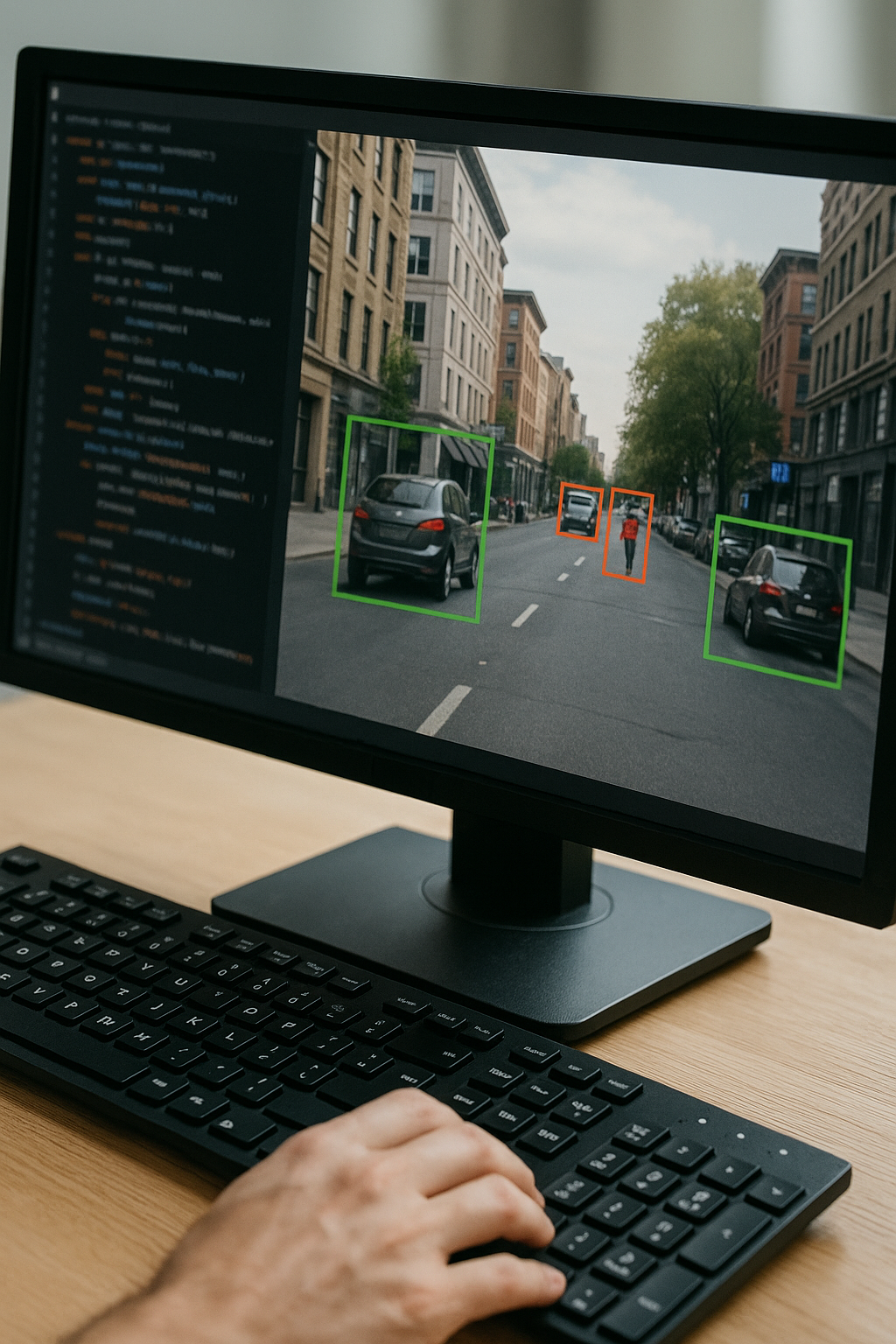
Fairness, Transparency, and Accountability in AI Systems
Building Trust in the Age of Machines (A Deep Dive)
Artificial intelligence (AI) is no longer science fiction; it's woven into the fabric of our daily lives. From the recommendation algorithms on your favourite streaming service to the spam filters in your email, AI silently shapes our experiences. While the potential benefits of AI are vast, from revolutionising healthcare to optimizing transportation systems, concerns about fairness, transparency, and accountability are rising.
Imagine a scenario where an AI-powered loan approval system systematically denies applications from a certain zip code, or a facial recognition technology used by law enforcement misidentifies a person, leading to wrongful arrest. These are just a few chilling examples of how AI algorithms, if not carefully designed and monitored, can perpetuate existing inequalities and injustices.
But fear not! By prioritizing fairness, transparency, and accountability in AI development, we can build trustworthy AI systems that benefit everyone, not just a privileged few. Let's take a deep dive into these crucial principles:
1. Fairness: Striving for Equity in AI Decisions
- Bias in the Machine: AI systems are only as fair as the data they are trained on. If the training data reflects societal biases (e.g., historical underrepresentation of certain demographics in loan applications), the AI system will likely perpetuate those biases in its decision-making.
- Mitigating Bias: Here's how we can combat bias in AI:
- Data Collection and Cleaning: Collecting diverse datasets that represent the real world and actively cleaning them for biases is crucial. This might involve oversampling underrepresented groups or removing sensitive information that could lead to bias.
- Fairness Metrics: Devising and implementing fairness metrics allows developers to identify and address potential biases in AI decision-making. These metrics could compare outcomes for different demographic groups or measure the disparity in error rates.
- Algorithmic Choice: Sometimes, choosing a different AI algorithm altogether can be a solution. For instance, simpler and more interpretable algorithms might be preferable for high-stakes applications like loan approvals, even if they are slightly less accurate than more complex models.
2. Transparency: Demystifying the AI Black Box
- The Explainability Challenge: Many AI algorithms, particularly complex deep learning models, function like black boxes. We input data, get an output, but the internal workings remain opaque. This lack of transparency can be problematic, especially when AI systems make critical decisions that impact people's lives.
- Explainable AI (XAI) Techniques: The field of Explainable AI (XAI) is developing techniques to shed light on how AI models arrive at their decisions. Here are a few examples:
- Feature Attribution: These methods highlight the specific features in the input data that most influenced the AI's decision.
- Counterfactual Explanations: XAI techniques can help us understand how a slight change in the input data would have impacted the output, offering insights into the model's reasoning process.
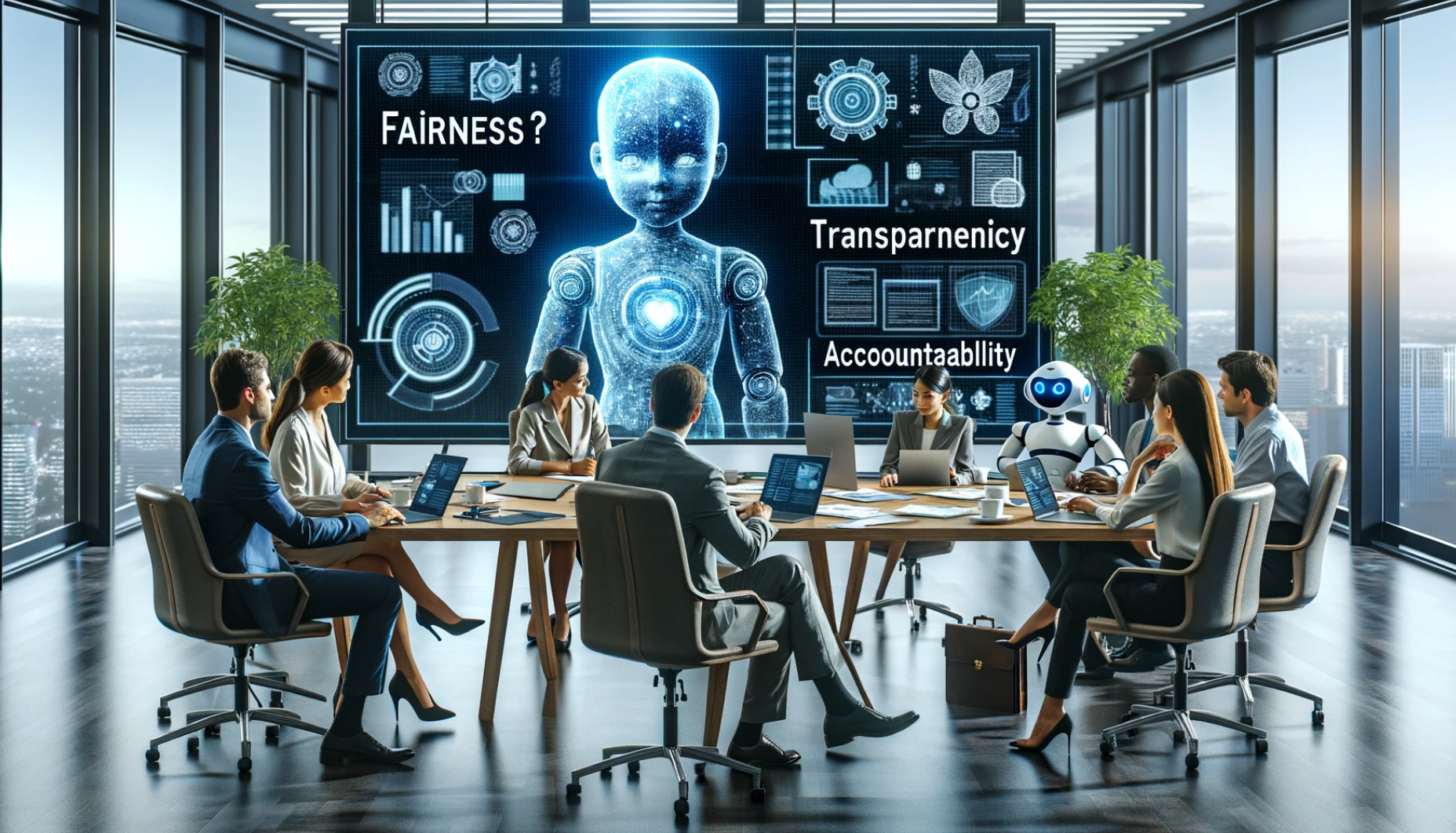

3. Accountability: Ensuring Someone is at the Wheel
- Who's Responsible? In a world increasingly reliant on AI, a crucial question emerges: who is accountable for the actions and decisions of these intelligent systems? Is it the developer, the company deploying the technology, or a combination of both?
- Shared Responsibility: A multi-pronged approach to accountability is necessary. Developers have a responsibility to build fair and robust AI systems, while companies deploying the technology need to ensure responsible use and implement safeguards to mitigate potential harms. Regulatory frameworks are also evolving to establish clear lines of accountability in the age of AI.
Building a Future of Responsible AI
These principles are not just lofty ideals; they are actionable steps towards building a future where AI empowers everyone. Here are some concrete ways to put them into practice:
- Diverse Development Teams: Building AI systems with teams that reflect the diversity of the population they will impact is crucial. A team with varied perspectives can help identify potential biases and ensure a more inclusive approach to AI development.
- Human oversight: While AI can automate tasks and make data-driven decisions, human oversight remains essential, especially for high-stakes applications. Humans can provide vital context and ethical considerations that AI systems currently lack.
- Regular Audits and Testing: Just like any complex system, AI models require regular audits for fairness and bias.Rigorous testing procedures should be implemented to identify and address potential issues before they cause harm.
Stay at the Forefront of the Responsible AI Movement
The field of responsible AI is constantly evolving, with new challenges and opportunities emerging. Sign up for our newsletter to receive the latest insights and developments in this critical area. Here's what you'll get:
- Practical guides on implementing responsible AI principles throughout your organization, from data collection to model deployment.
- Curated newsfeeds with the latest industry news, research breakthroughs, and upcoming events related to responsible AI.
Join us on the journey towards a future where AI empowers everyone! Subscribe to our newsletter and be a part of building a more responsible and equitable future with AI. Together, we can ensure that AI becomes a force for good,driving progress and prosperity for all.
Sign Up For Our Weekly Newsletter and Get Your FREE Ebook " AI For Everyone - Learn the Basics and Embrace the Future"