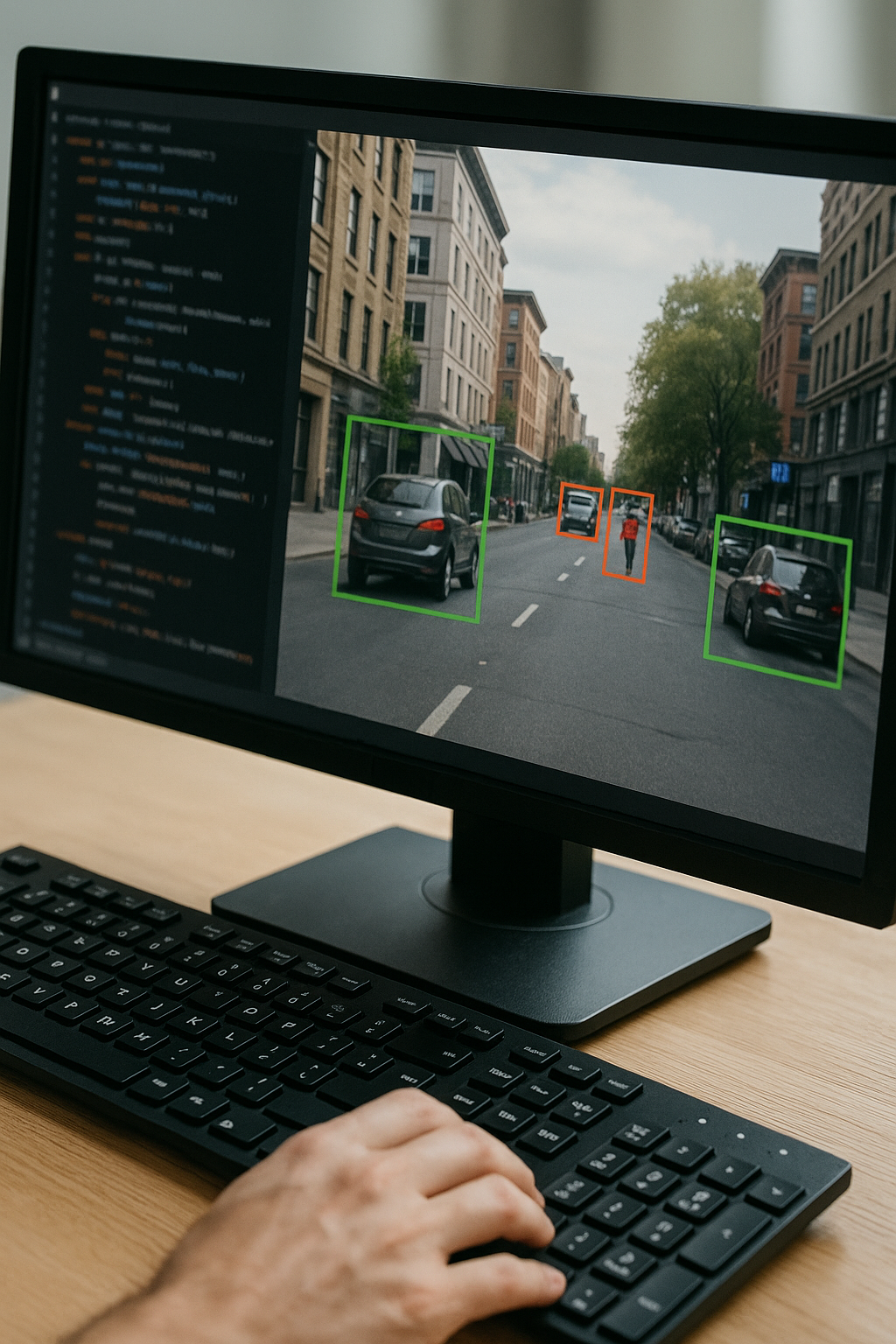
The Future of Work: AI’s Impact on Job Markets and Skills
AI is no longer confined to labs; it’s deeply integrated into modern business operations. By automating routine processes, delivering predictive insights, and enabling personalized experiences, AI is driving profound change across industries. In this expanded exploration, we’ll examine the nuances of job displacement, the emergence of new career paths, and the multifaceted skillsets workers need to thrive in an AI-augmented economy.
The Dual Nature of Automation: Disruption and Opportunity
High-Risk Roles
AI excels at pattern recognition, data entry, and rule-based tasks. Roles most exposed include:
- Administrative Support: Automated calendar management, email triage, and document generation reduce demand for entry-level assistants.
- Transactional Finance: RPA systems process invoices, reconcile accounts, and detect anomalies faster than manual teams.
- Customer Service: Chatbots and virtual agents handle tier-one inquiries, freeing human agents for complex escalations.
Augmented Professions
Rather than outright replacement, many roles will evolve through AI augmentation:
- Marketing Analysts gain real-time audience segmentation tools but must guide AI insights into coherent campaigns.
- Manufacturing Technicians collaborate with AI-driven quality-control systems, using machine vision alerts to adjust production lines.
- Healthcare Providers utilize diagnostic algorithms for early disease detection while focusing on patient care and treatment planning.
Zero-Sum vs. Growth Models
While some estimates predict net job losses in certain sectors, others highlight how AI drives economic expansion and new job creation. For every traditional role displaced, multiple indirect roles—such as data stewardship, AI compliance auditing, and machine maintenance—are emerging.
Emerging Roles and Growth Sectors
AI Strategy and Governance
As organizations integrate AI, strategic leadership roles are crucial:
- Chief AI Officer (CAIO): Aligns AI initiatives with business objectives and ensures ROI.
- AI Ethics Manager: Oversees bias audits, transparency measures, and regulatory compliance.
- Data Protection Officer: Manages data privacy, cybersecurity frameworks, and cross-border data flows.
Human-Centric AI Experts
Bridging the gap between technology and people, these roles focus on adoption, usability, and training:
- AI UX Designer: Crafts interfaces that translate complex AI outputs into intuitive user experiences.
- Learning Facilitator: Develops curricula on AI tools, fostering digital literacy and change management.
- Collaboration Coach: Guides teams on best practices for human-AI partnerships, optimizing hybrid workflows.
Sector-Specific Innovators
Domain experts who leverage AI within industry contexts:
- Precision Agriculture Analyst: Uses predictive agronomic models to optimize crop cycles and sustainable resource use.
- Legal Tech Developer: Builds AI-driven contract analysis tools, e-discovery systems, and compliance monitors.
- Financial Modeler: Integrates AI into risk assessment, portfolio optimization, and fraud detection.

The New Skill Ecosystem
Foundational Digital Skills
- Data Literacy: Ability to interpret dashboards, query databases, and understand model limitations.
- Tool Proficiency: Familiarity with AI platforms (e.g., TensorFlow, Azure AI) and low-code/no-code automation solutions.
Complex Problem-Solving and Critical Thinking
AI systems can surface insights, but human analysts must frame questions, evaluate model validity, and reconcile conflicting data. Scenario planning and ethical reasoning become central to decision-making.
Creative and Strategic Competencies
As AI takes over repetitive tasks, humans excel in roles requiring ideation, narrative building, and ecosystem design. Strategic foresight—anticipating AI-driven market shifts—will differentiate leaders.
Interpersonal and Adaptive Expertise
Emotional intelligence, cross-cultural communication, and change leadership will determine success in AI-infused workplaces. The capacity to unlearn outdated processes and embrace continuous feedback loops is crucial.
Building a Future-Ready Organization
Talent Development Frameworks
Companies should establish lifelong learning programs, micro-credential pathways, and AI mentorship circles. By tracking skill progress through internal badges and project rotations, organizations can pivot talent into emerging AI roles.
Ecosystem Partnerships
Collaborations with universities, bootcamps, and online platforms ensure curricula keep pace with technological advances. Public–private initiatives—such as AI apprenticeships—offer structured on-the-job training tied to real outcomes.
Navigating Ethical and Societal Dimensions
The rapid adoption of AI demands holistic governance:
- Transparency: Clear communication about how AI influences hiring, performance reviews, and customer interactions.
- Equity: Proactive measures to prevent algorithmic bias and ensure inclusive access to AI-driven opportunities.
- Safety Nets: Policies like wage insurance, skills escrow accounts, and community reskilling centers mitigate transitional hardships.
Preparing for the Next Wave: Quantum AI and Beyond
Emerging technologies will compound AI’s impact:
- Quantum Computing: May revolutionize optimization, material discovery, and cryptography, spawning specialized quantum algorithm engineers.
- Edge AI: Real-time inference on devices from IoT sensors to wearables creates roles in secure edge deployment and federated learning architecture.
Conclusion
AI’s transformative power will redefine work, but human ingenuity remains at the heart of innovation. By understanding disruption patterns, cultivating future-proof skills, and fostering ethical governance, we can shape an inclusive, dynamic labor market.
Eager to navigate your AI career journey? Subscribe to our newsletter for monthly deep dives and skill-building roadmaps straight to your inbox.
Sign Up For Our Weekly Newsletter and Get Your FREE Ebook " AI For Everyone - Learn the Basics and Embrace the Future"