AI in Transportation
Self-driving Cars, Autonomous Vehicles, and Urban Mobility Solutions
The dawn of a new era in transportation is upon us, driven by the relentless advancement of artificial intelligence (AI). From the bustling streets of metropolitan hubs to the vast expanse of interstate highways, AI is revolutionizing how we conceive, implement, and experience mobility. This technological renaissance promises to reshape our cities, redefine our relationship with vehicles, and fundamentally alter the fabric of our daily lives. Let's embark on a comprehensive exploration of AI's role in transportation, delving into the intricacies of self-driving cars, the broader implications of autonomous vehicles, and the innovative urban mobility solutions that are transforming our cityscapes.
Self-Driving Cars: The Vanguard of AI in Transportation
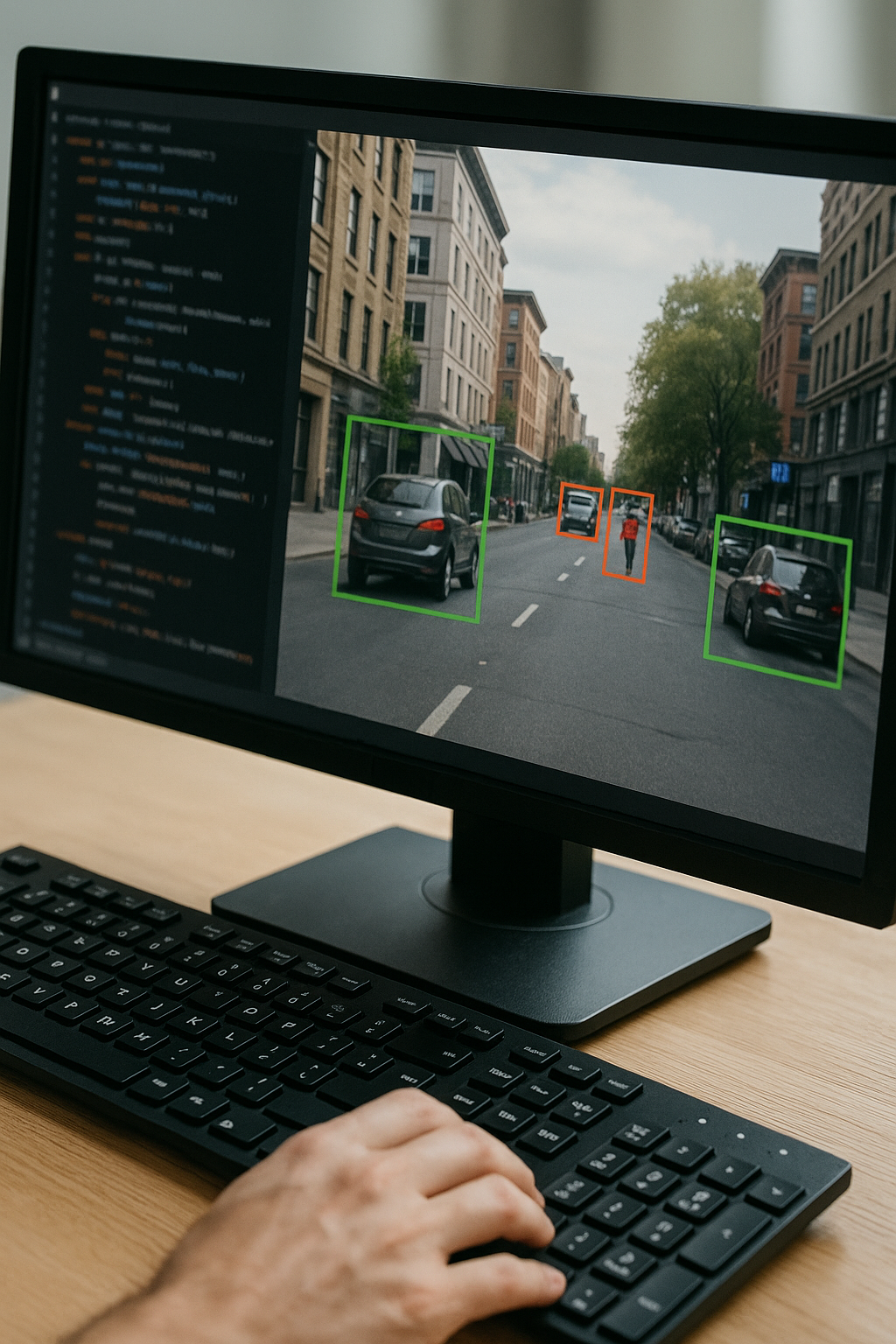
At the forefront of this transportation revolution are self-driving cars, vehicles that leverage a sophisticated array of technologies to navigate the world without human intervention. These marvels of modern engineering represent the culmination of decades of research and development, bringing together advancements in computer vision, machine learning, sensor technology, and more.
The Technological Tapestry of Autonomy
Self-driving cars rely on a complex ecosystem of sensors and AI algorithms to perceive and interact with their environment. At the heart of this system are:
- LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging): This technology uses laser pulses to create a detailed 3D map of the vehicle's surroundings, allowing for precise distance measurements and object detection.
- Radar: Complementing LiDAR, radar systems help detect the speed and direction of moving objects, crucial for predicting the behavior of other vehicles and pedestrians.
- Cameras: High-resolution cameras provide visual information, allowing the AI to recognize traffic signs, lane markings, and other important visual cues.
- Ultrasonic Sensors: These sensors assist with close-range object detection, particularly useful for parking and low-speed maneuvering.
- GPS and IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit): These systems work together to provide precise location and orientation data, essential for navigation and route planning.
The data from these sensors is processed by powerful onboard computers running sophisticated AI algorithms. These algorithms use techniques like deep learning and computer vision to interpret the sensor data, make decisions, and control the vehicle's actions in real-time.
Levels of Autonomy: The Path to Full Self-Driving
The Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) has defined six levels of driving automation, from Level 0 (no automation) to Level 5 (full automation). As of 2024, most commercially available vehicles with "self-driving" features fall into Levels 2 or 3, offering advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) that can handle specific tasks but still require human oversight.
Level 2 systems, like Tesla's Autopilot or General Motors' Super Cruise, can control steering, acceleration, and braking in certain scenarios, but the driver must remain alert and ready to take control at any moment. Level 3 systems, such as those being developed by Audi and Mercedes-Benz, can handle more complex scenarios and allow the driver to disengage in certain conditions, but still require the ability to retake control when prompted.
The holy grail of self-driving technology is Level 5 autonomy, where the vehicle can operate without any human intervention under all conditions. While this level of autonomy remains on the horizon, companies like Waymo (a subsidiary of Alphabet) and Cruise (backed by General Motors) are making significant strides towards this goal, with pilot programs of highly autonomous vehicles operating in select cities.
The Promise and Potential of Self-Driving Cars
The widespread adoption of self-driving cars holds the potential to revolutionize personal transportation in numerous ways:
- Enhanced Safety: By eliminating human error, which is responsible for the vast majority of traffic accidents, self-driving cars could dramatically reduce road fatalities and injuries.
- Increased Accessibility: Autonomous vehicles could provide unprecedented mobility to those unable to drive due to age, disability, or other factors.
- Improved Efficiency: AI-controlled vehicles can optimize routes, reduce traffic congestion, and potentially decrease fuel consumption and emissions.
- Redefined Car Ownership: The advent of self-driving cars could shift the paradigm from personal car ownership to mobility-as-a-service models, potentially reducing the number of vehicles on the road and freeing up urban space currently dedicated to parking.
- Productivity Gains: As vehicles take over the task of driving, passengers could use their commute time for work, relaxation, or entertainment.

Autonomous Vehicles: Beyond Personal Transportation
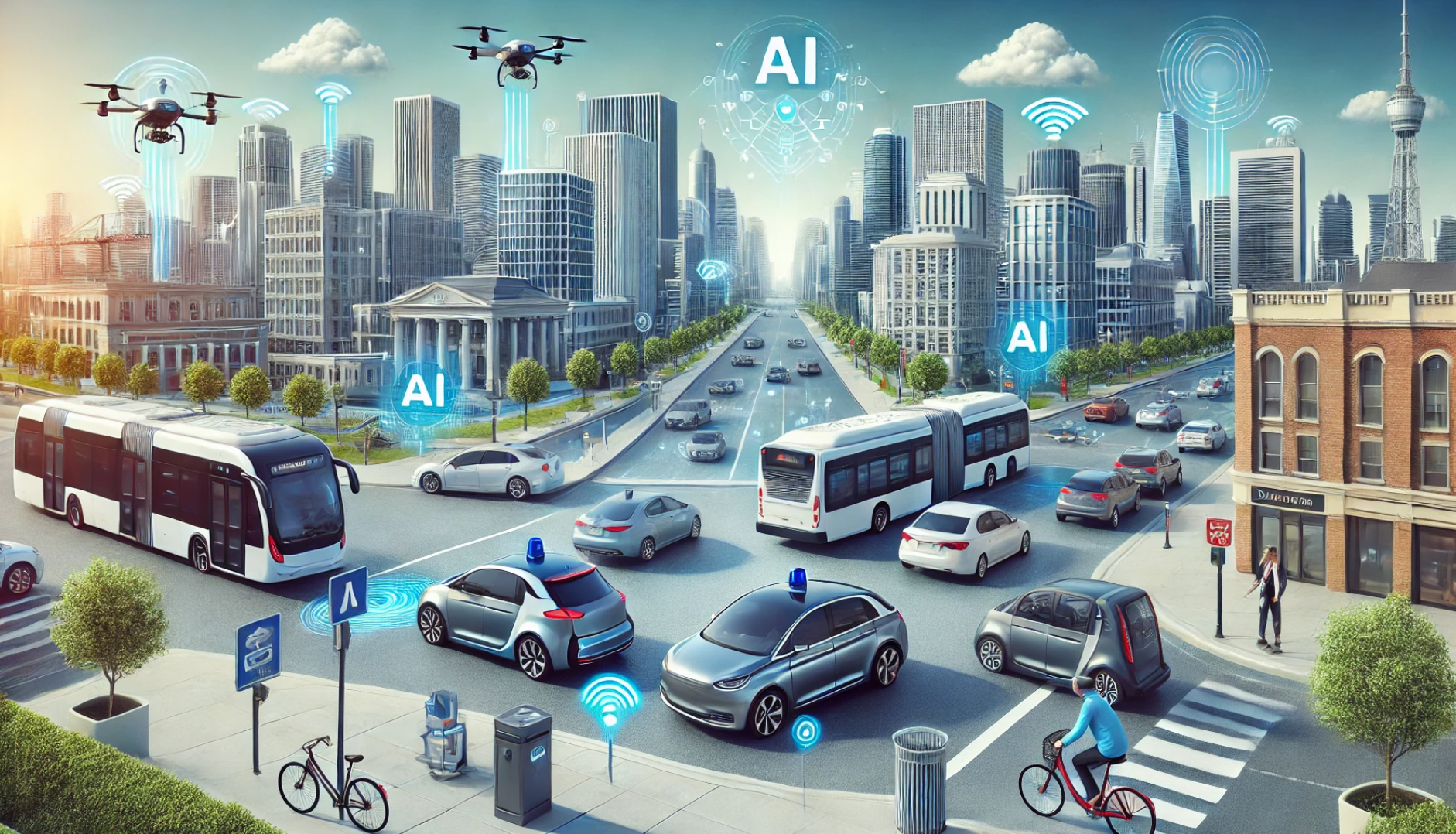
While self-driving cars capture much of the public's imagination, the application of AI in transportation extends far beyond personal vehicles. The concept of autonomous vehicles encompasses a wide range of applications that are set to transform various sectors of the transportation industry.
Revolutionizing Logistics with Autonomous Trucks
The trucking industry stands on the brink of a major transformation with the advent of autonomous trucks. Companies like TuSimple, Embark, and Plus are developing self-driving technologies specifically for long-haul trucking, aiming to address critical issues facing the industry:
- Driver Shortages: Autonomous trucks could help alleviate the chronic shortage of truck drivers, a problem that has plagued the industry for years.
- Improved Efficiency: AI-driven trucks can operate for longer hours, optimizing delivery schedules and potentially reducing shipping times and costs.
- Enhanced Safety: By eliminating driver fatigue and human error, autonomous trucks could significantly reduce accidents involving heavy vehicles.
- Fuel Efficiency: AI systems can optimize driving patterns for maximum fuel efficiency, potentially reducing the environmental impact of long-haul shipping.
While fully autonomous trucks operating without any human oversight are still in development, many companies are implementing "platooning" technologies. This involves a lead truck operated by a human driver followed closely by one or more autonomous trucks, increasing efficiency and safety while still maintaining human oversight.
Transforming Public Transit with Autonomous Buses and Shuttles
In urban and suburban areas, autonomous buses and shuttles are being tested as potential solutions to enhance public transportation:
- Flexible Routes: AI-powered buses can dynamically adjust their routes based on real-time demand, potentially providing more efficient and responsive service.
- Extended Service Hours: Autonomous vehicles could make it economically feasible to provide public transportation services during off-peak hours when operating traditional buses might be cost-prohibitive.
- First/Last Mile Solutions: Small autonomous shuttles could bridge the gap between major transit hubs and final destinations, solving the "last mile" problem in public transportation.
- Improved Accessibility: Autonomous vehicles with specialized designs could better serve passengers with mobility challenges, providing more independence and freedom of movement.
Cities like Singapore, Helsinki, and Las Vegas have already begun testing autonomous shuttle services, providing valuable data on the integration of these vehicles into existing urban transportation networks.
The Rise of Autonomous Aerial Vehicles
The concept of autonomous vehicles isn't limited to ground transportation. Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs), or drones, are increasingly being developed for a variety of transportation applications:
- Package Delivery: Companies like Amazon and Google are developing drone delivery systems that could revolutionize last-mile logistics, particularly in hard-to-reach areas.
- Emergency Services: Autonomous drones could be used to deliver medical supplies, conduct search and rescue operations, or provide real-time information during disaster response efforts.
- Passenger Transport: While still in early stages, companies are developing autonomous "flying taxis" that could provide rapid point-to-point transportation in urban areas, potentially alleviating ground traffic congestion.
- Infrastructure Inspection: Autonomous drones are already being used to inspect bridges, power lines, and other critical infrastructure, improving safety and efficiency in maintenance operations.
As regulations evolve and technology advances, the integration of autonomous aerial vehicles into our transportation ecosystem could open up new dimensions in urban mobility and logistics.
Urban Mobility Solutions: AI for Smarter Cities
As urbanization continues to accelerate globally, cities face increasing challenges in managing transportation infrastructure and meeting the mobility needs of growing populations. Artificial intelligence is playing a crucial role in developing smart urban mobility solutions that can adapt to the changing needs of city dwellers and create more sustainable, efficient, and livable urban environments.
Intelligent Traffic Management Systems
One of the most impactful applications of AI in urban transportation is in the development of intelligent traffic management systems. These systems leverage a network of sensors, cameras, and AI algorithms to optimize traffic flow in real-time:
- Adaptive Traffic Signals: AI-powered traffic lights can adjust their timing based on real-time traffic conditions, reducing congestion and minimizing wait times at intersections.
- Predictive Traffic Modeling: By analyzing historical data and real-time inputs, AI systems can predict traffic patterns and proactively adjust traffic management strategies to prevent congestion before it occurs.
- Incident Detection and Response: AI algorithms can quickly identify traffic incidents or accidents and automatically alert emergency services and adjust traffic patterns to minimize disruption.
- Dynamic Lane Management: Some cities are implementing AI-controlled dynamic lane systems that can change the direction of traffic flow based on demand, maximizing the efficiency of existing road infrastructure.
- Connected Vehicle Integration: As more vehicles become equipped with V2X (Vehicle-to-Everything) communication capabilities, traffic management systems can communicate directly with individual vehicles, providing real-time routing suggestions and warnings about upcoming hazards or congestion.
Cities like Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania have implemented AI-driven traffic management systems and have seen significant reductions in travel times and emissions as a result.
Optimizing Public Transportation with AI
Artificial intelligence is also being leveraged to enhance the efficiency and user experience of public transportation systems:
- Demand Prediction: By analyzing historical ridership data, weather patterns, and special events, AI systems can predict demand for public transportation services, allowing transit authorities to adjust service levels accordingly.
- Real-Time Service Adjustments: AI algorithms can monitor the entire transit network in real-time, identifying delays or disruptions and automatically adjusting schedules or suggesting alternative routes to minimize passenger impact.
- Predictive Maintenance: AI-powered systems can analyze data from sensors on buses, trains, and infrastructure to predict when maintenance will be needed, reducing downtime and improving overall system reliability.
- Personalized Trip Planning: AI-driven mobile apps can provide passengers with personalized trip recommendations based on their preferences, real-time transit conditions, and even factors like carbon footprint.
- Accessibility Enhancements: AI can be used to improve transit accessibility for passengers with disabilities, such as providing real-time audio guidance for visually impaired users or optimizing wheelchair-accessible route planning.
Cities like London and Tokyo are at the forefront of implementing these AI-driven solutions to manage their complex public transportation networks more effectively.
Revolutionizing Parking with Smart Systems
Parking is a significant challenge in urban areas, contributing to congestion, emissions, and frustration for drivers. AI is being employed to create smart parking solutions that can alleviate these issues:
- Real-Time Parking Availability: AI-powered systems using camera networks or sensor data can provide real-time information on parking availability, guiding drivers directly to open spots and reducing time spent searching.
- Predictive Parking: By analyzing historical data and real-time factors, AI can predict parking availability at different times and locations, allowing drivers to plan their trips more effectively.
- Dynamic Pricing: AI systems can implement dynamic pricing strategies for parking, adjusting rates based on demand to optimize space utilization and potentially reduce overall parking demand.
- Automated Parking Enforcement: AI-powered camera systems can automate parking enforcement, improving compliance and reducing the need for human parking attendants.
- Autonomous Valet Parking: Some car manufacturers are developing autonomous valet parking systems that allow vehicles to park themselves in specially equipped garages, maximizing space utilization and improving convenience for drivers.
Cities like San Francisco and Barcelona have implemented smart parking systems, resulting in reduced congestion and improved urban mobility.
Micromobility and Last-Mile Solutions
AI is playing a crucial role in the rise of micromobility solutions like shared bikes and e-scooters, which are increasingly important for solving the "last mile" problem in urban transportation:
- Demand Prediction and Rebalancing: AI algorithms analyze usage patterns to predict demand and optimize the distribution of shared bikes and scooters across a city.
- Dynamic Pricing: Similar to ride-sharing services, AI can implement dynamic pricing for micromobility services to balance supply and demand.
- Safety Enhancements: AI-powered systems in e-scooters can detect unsafe riding behaviors or inappropriate parking, helping to address common concerns about these services.
Cities like Paris and Singapore have successfully integrated AI-powered micromobility solutions into their broader urban transportation strategies, providing residents with more flexible and sustainable mobility options.
Challenges and Considerations in AI-Driven Transportation
While the potential benefits of AI in transportation are enormous, the path to widespread adoption is not without obstacles. Several key challenges and considerations must be addressed as we move towards an AI-driven transportation future:
Safety and Reliability
Ensuring the safety and reliability of AI-driven transportation systems is paramount. This includes:
- Edge Case Handling: AI systems must be capable of handling rare and unexpected situations, often referred to as "edge cases," which can be challenging to anticipate and program for.
- Weather and Environmental Challenges: Autonomous vehicles must be able to operate safely in all weather conditions and diverse environments, from dense urban areas to rural landscapes.
- Interaction with Human-Driven Vehicles: During the transition period, AI-driven vehicles will need to safely interact with human-driven vehicles, pedestrians, and other road users who may behave unpredictably.
- System Redundancy and Fail-Safes: AI transportation systems must incorporate robust redundancies and fail-safe mechanisms to ensure safety in the event of system failures or malfunctions.
Ethical Considerations
The development of AI in transportation raises several ethical questions that need to be addressed:
- Decision-Making in Unavoidable Accidents: How should autonomous vehicles be programmed to react in situations where an accident is unavoidable but different outcomes affect different individuals.
- Equitable Access: As transportation becomes increasingly AI-driven and potentially more efficient, how do we ensure equitable access to these benefits across all segments of society?
- Job Displacement: The widespread adoption of autonomous vehicles could lead to significant job losses in the transportation sector. How can society manage this transition and support affected workers?
The rapid advancement of AI in transportation is outpacing existing regulatory frameworks, creating challenges for policymakers:
- Liability in Accidents: Determining liability in accidents involving autonomous vehicles is a complex issue that requires new legal frameworks.
- Standardization and Interoperability: As different companies develop autonomous technologies, ensuring standardization and interoperability between systems becomes crucial for widespread adoption.
- Data Governance: Regulations around the collection, use, and sharing of data generated by AI transportation systems need to be developed and enforced.
- Cross-Border Operations: For long-haul trucking and international travel, harmonizing regulations across different jurisdictions will be necessary.
Cybersecurity
As transportation systems become increasingly connected and AI-driven, they also become more vulnerable to cyber threats:
- Hacking and Malicious Interference: Protecting autonomous vehicles and transportation infrastructure from hacking attempts that could compromise safety or disrupt services is a critical concern.
- Data Protection: Safeguarding the vast amounts of data collected by AI transportation systems from theft or unauthorized access is essential.
- System Resilience: Developing AI systems that can detect and respond to cyber attacks in real-time, maintaining safe operation even under adverse conditions.
Infrastructure Adaptation
Integrating AI-driven transportation solutions often requires updates to existing infrastructure:
- Smart Road Infrastructure: Implementing sensors, communication systems, and other technologies to support autonomous vehicles and intelligent traffic management.
- Charging Infrastructure: As transportation electrification goes hand-in-hand with autonomy, developing adequate charging infrastructure becomes crucial.
- Data Infrastructure: Building the necessary data collection, processing, and storage infrastructure to support AI-driven transportation systems.
- Urban Planning: Rethinking urban design to accommodate new modes of transportation and changing patterns of mobility.
Public Acceptance and Trust
Gaining public trust and acceptance of AI-driven transportation solutions is crucial for widespread adoption:
- Transparency: Providing clear information about how AI systems make decisions and ensuring accountability in case of failures or accidents.
- User Education: Educating the public about the capabilities and limitations of AI-driven transportation systems to set realistic expectations and promote safe usage.
- Demonstrating Benefits: Clearly communicating and demonstrating the tangible benefits of AI in transportation to the public, such as improved safety, efficiency, and accessibility.
- Addressing Fears and Misconceptions: Proactively addressing common fears and misconceptions about AI-driven transportation through public engagement and education initiatives.
The Road Ahead: Embracing the AI-Driven Transportation Revolution
As we stand on the cusp of this transportation revolution, the potential for AI to transform how we move and shape our cities is truly awe-inspiring. From self-driving cars that promise to make our roads safer and more efficient, to intelligent urban mobility solutions that could redefine the very fabric of our cities, the future of transportation is brimming with possibilities.
But this future isn't a distant dream - it's unfolding right before our eyes. Today, you can experience the early stages of this revolution firsthand. Many car manufacturers are offering vehicles with advanced driver assistance systems that represent the first steps towards full autonomy. Why not take one for a test drive and get a taste of what the future holds?
For those living in urban areas, the AI revolution in transportation is already making waves. From smart parking apps that can guide you to available spots, to AI-optimized bike-sharing systems that ensure a ride is always nearby, these technologies are reshaping urban mobility.
Sign Up For Our Weekly Newsletter and Get Your FREE Ebook " AI For Everyone - Learn the Basics and Embrace the Future"