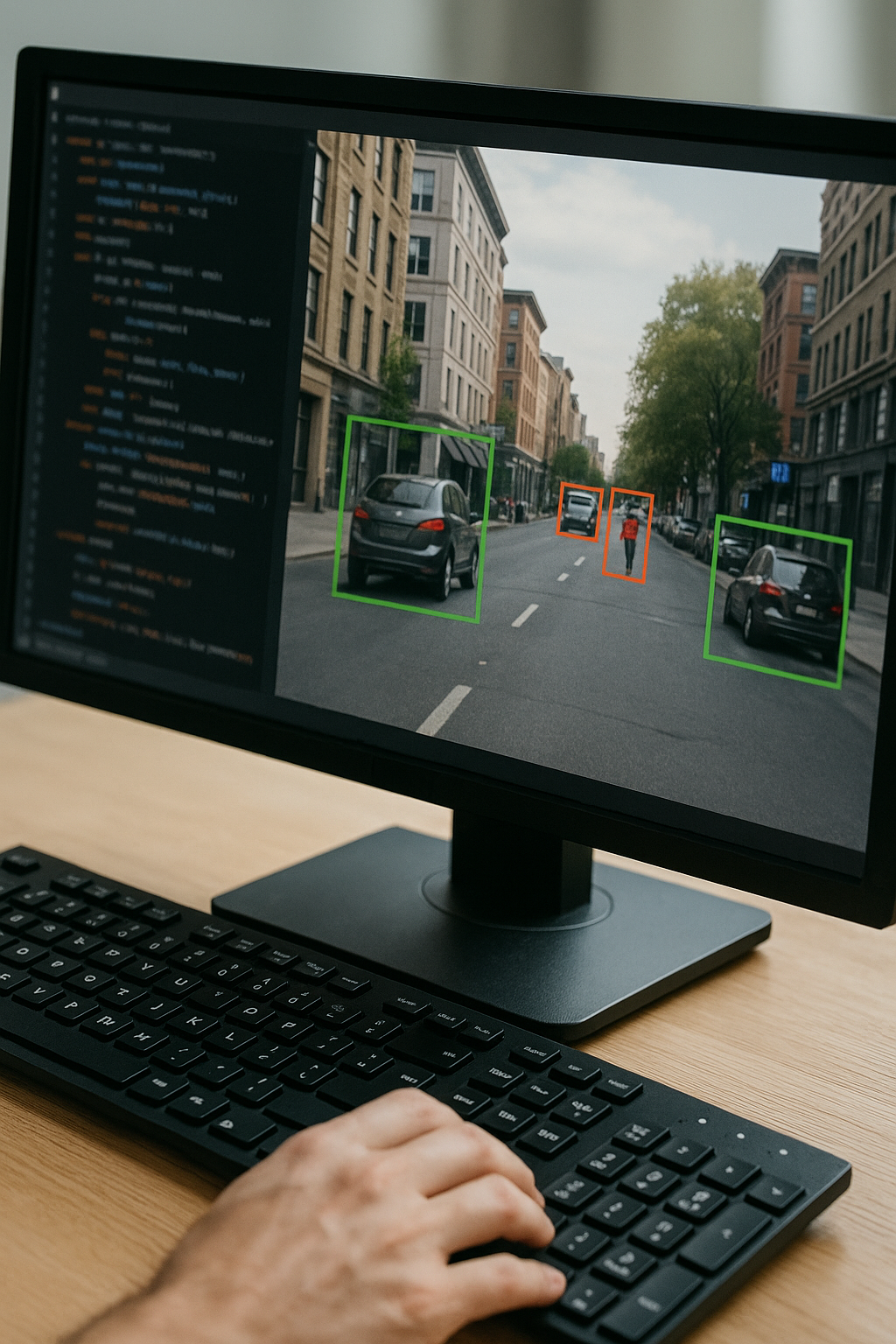
AI vs. Machine Learning
Decoding the Digital Revolution's Core Technologies
The Technological Frontier
In the rapidly evolving landscape of digital innovation, two terms have emerged as pivotal pillars of technological transformation: Artificial Intelligence AI and Machine Learning (ML). While often used interchangeably, these concepts represent distinct yet deeply interconnected approaches to creating intelligent systems that are reshaping our world.
This comprehensive guide will unravel the intricate relationship between AI and Machine Learning, providing technology enthusiasts, professionals, and curious minds with an in-depth understanding of these groundbreaking technologies.
The Expansive Realm of Artificial Intelligence
Defining Artificial Intelligence: Beyond Simple Computation
Artificial Intelligence represents the broader vision of creating machines capable of mimicking human cognitive functions. It's not just about programming computers to perform tasks, but about developing systems that can:
- Reason and problem-solve
- Understand and process natural language
- Recognize complex patterns
- Make autonomous decisions
- Adapt to dynamic environments
Historical Context: The concept of AI dates back to the 1950s, when pioneering computer scientists like Alan Turing proposed the revolutionary idea that machines could potentially "think" and simulate human intelligence.
Branches of Artificial Intelligence
Narrow AI (Weak AI)
- Designed for specific tasks
- Examples: Virtual assistants, recommendation systems, image recognition software
- Operates within a predefined range of functions
General AI (Strong AI)
- Theoretical systems with human-like cognitive abilities
- Capable of learning and applying intelligence across diverse domains
- Currently more of a research aspiration than a practical reality
Superintelligent AI
- Hypothetical systems surpassing human intelligence
- Remains a topic of philosophical and technological speculation

Machine Learning: The Adaptive Learning Paradigm
Understanding Machine Learning's Fundamental Mechanics
Machine Learning is a specialized subset of AI focused on developing algorithms that can learn and improve from experience without explicit programming. Unlike traditional software that follows rigid, predefined rules, ML systems evolve by analyzing and extracting insights from data.
Core Machine Learning Approaches
Supervised Learning
- Algorithms trained on labeled datasets
- Learn to map input data to known output labels
- Applications: Spam detection, image classification, price prediction
Unsupervised Learning
- Works with unlabeled data
- Discovers hidden patterns and structures
- Applications: Customer segmentation, anomaly detection, recommendation systems
Reinforcement Learning
- Learning through interaction with an environment
- Systems receive rewards or penalties based on actions
- Applications: Game AI, robotics, autonomous vehicle navigation
Practical Differentiation: AI vs. Machine Learning
Conceptual Distinctions
- AI: The overarching goal of creating intelligent machines
- Machine Learning: A specific approach to achieving AI through data-driven learning
Real-World Analogy
Imagine AI as the vision of creating a perfect chef, and Machine Learning as the process of teaching that chef by exposing them to countless recipes, techniques, and cooking experiences.
Transformative Applications Across Industries
Healthcare
AI Vision: Comprehensive diagnostic and treatment systems
ML Implementation:
- Medical image analysis
- Predictive disease modeling
- Personalized treatment recommendations
Finance
AI Vision: Intelligent financial decision-making systems
ML Implementation:
- Fraud detection
- Algorithmic trading
- Risk assessment models
Transportation
AI Vision: Fully autonomous transportation ecosystems
ML Implementation:
- Self-driving vehicle navigation
- Traffic prediction
- Route optimization
Emerging Trends and Future Outlook
Convergence of Technologies
- Integration of AI, ML, and other emerging technologies
- Increased focus on ethical AI development
- Growing emphasis on explainable and transparent algorithms
Challenges and Considerations
- Data privacy concerns
- Algorithmic bias
- Computational limitations
- Ethical implementation of intelligent systems
The Human Element: Collaboration, Not Replacement
Despite technological advancements, the most powerful systems will emerge from human-AI collaboration. Machine Learning and AI are tools designed to augment human capabilities, not to replace human creativity and critical thinking.
Your Gateway to Technological Insight
The world of AI and Machine Learning is evolving at an unprecedented pace. Breakthroughs are happening daily, reshaping industries, solving complex problems, and opening unprecedented opportunities for innovation.
Ready to stay ahead of the technological curve?
Sign Up For Our Weekly Newsletter and Get Your FREE Ebook " AI For Everyone - Learn the Basics and Embrace the Future"
Don't just watch the future unfold—be part of understanding and shaping it.
Note to Readers: Technology is a dynamic landscape. The insights shared here represent our current understanding, and the field of AI and Machine Learning continues to evolve rapidly.